CI/CD for Apps Developed on AI Platform
This page covers how to set up continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) for applications developed on the Acme AI Platform.
Application setup
Architecture
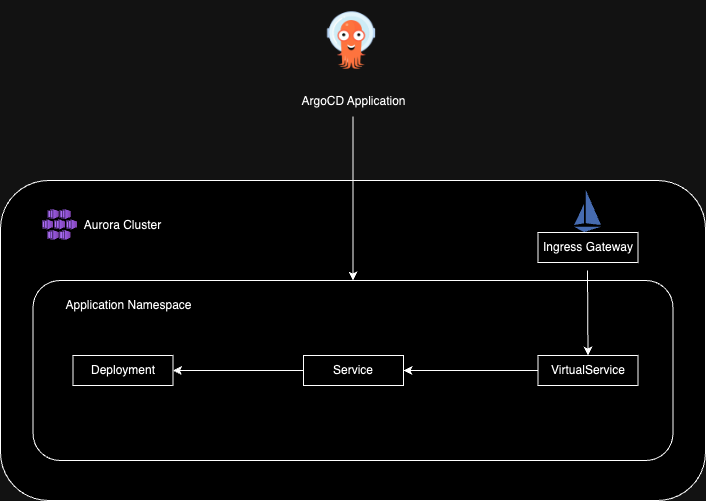 Architecture diagram
Architecture diagram
Repository Structure
List of folders within the app's repository:
.github/workflows: contains GitHub Action workflows for continuous integration and spell checking in pull requests. Since a portion of the repository is documentation, the spell check action is not required for the sample application.app/: contains the Python Flask application (sample app).helm/: contains the Helm application used for continuous deployment setup. The Argo CD application will target this directory to deploy user workloads to an AI Platform cluster.
Setting up an Azure Container Registry
The repository's continuous integration workflow references an Azure Container Registry (ACR), requiring developers to insert their own secrets to produce images. AI Platform fetches images from multiple ACRs deployed across different subscriptions:
| Registry | Subscription |
|---|---|
| auroradevacr.azurecr.io | S913-Aurora-Non-production |
| auroraprodacr.azurecr.io | S040-Aurora-Production |
Application developers should set the REGISTRY_PASSWORD and REGISTRY_USERNAME as GitHub repository secrets, and define the REGISTRY, PROJECT, and NAME environment variables that will be used to form the image tag.
Example:
- REGISTRY:
auroraprodacr.azurecr.io - PROJECT:
training - NAME:
aurora-flask-app
And the secrets should be set as shown in the following image:
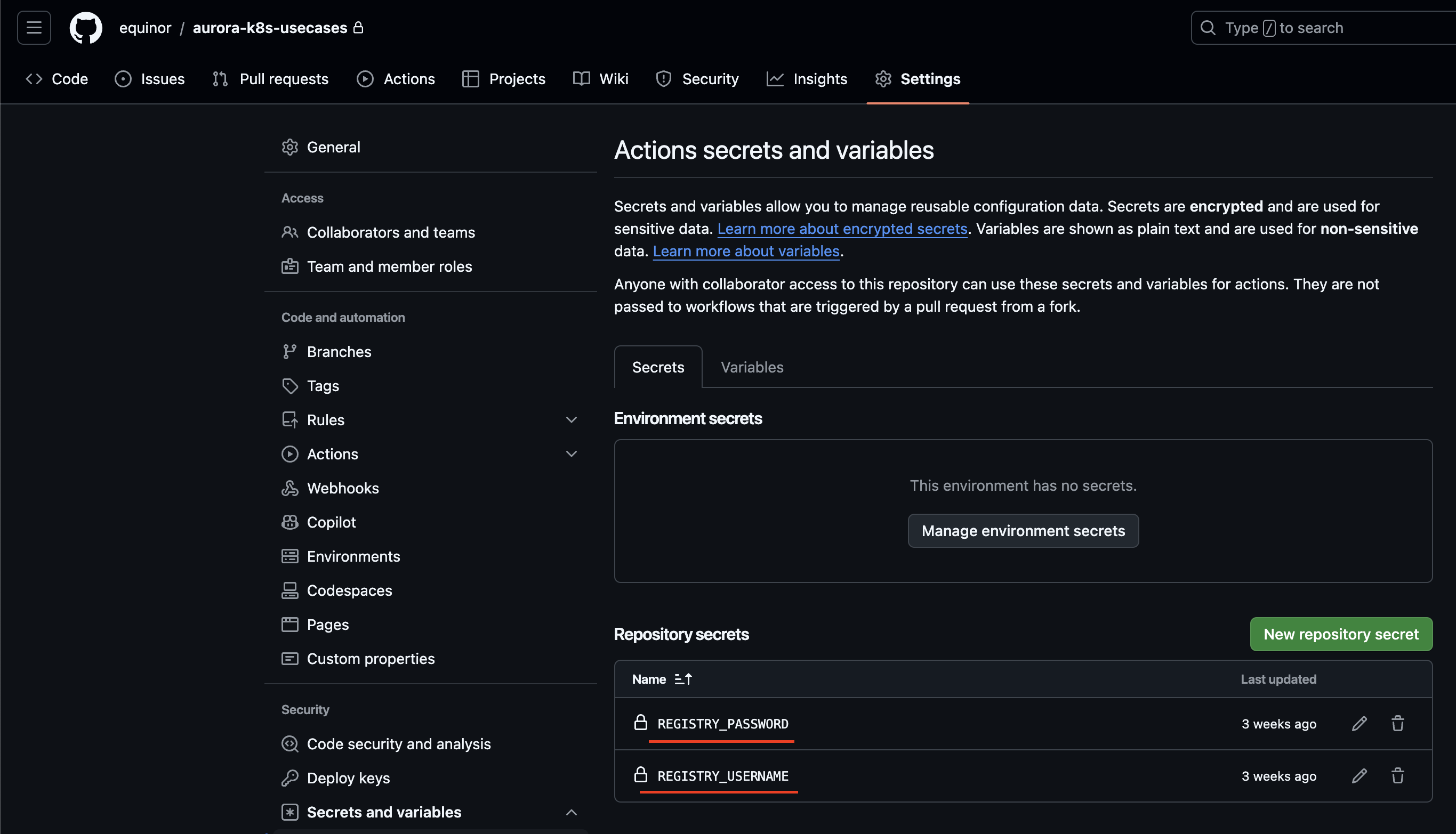 GitHub settings
GitHub settings
In this case, the workflow will produce an image with the latest tag and push it to the auroraprodacr.azurecr.io/training/aurora-flask-app repository when the code is merged into the main branch.
AI Platform developers are not permitted to grant access to ACRs themselves. Therefore, the only option is to contact the #ai_platfrom_support Slack channel with the request.
In accordance with the least privilege access security practice, AI Platform administrators will create an ACR token and scope map tailored to your specific needs. Therefore, you must provide a strict list of the repositories to which you will be pushing images.
Continuous Integration with GitHub Actions
Based on the repository structure, there is a GitHub workflows folder containing several YAML files. Among them is CI.yaml, a workflow designed to build and push images to an Azure container registry. This workflow is configured to monitor any changes in the app/ folder of the main branch, as well as changes to the workflow file itself.
Developers can reuse this workflow by modifying the environment variables and setting their repository secrets to enable pushing to the container registry. Go to Setting up Azure Container Registry for details.
In case of bigger apps with more demanding builds you can either use GitHub-hosted large runners (code snippet example), or set up self-hosted runners with the desired size
Continuous deployment with Argo CD
For continuous deployment, AI Platform uses Argo CD .
AI Platform provides two Argo CD servers in different environments:
| Argo CD endpoint | Subscription |
|---|---|
<https://dashboard.internal.aurora.equinor.com> | S913-Aurora-Non-production |
<https://dashboard.aurora.equinor.com> | S040-Aurora-Production |
To prevent access to sensitive information between projects, access is restricted across projects. Therefore, developers must first submit a support request to the #ai_platfrom_support Slack channel to onboard their application to Argo CD. The following information is required:
- project name and WBS
- target cluster
- repository URL (SSH key generation may be required to add the repository to Argo CD)
- Azure Entra ID Group ID that should have access to the application resources
Upon resolution of the support request, developers who belong to the Entra ID group will be able to perform CRUD operations on applications within their Argo CD projects and manage cluster resources, including direct access with kubectl if requested.
How to create an Argo CD Application
Install and log in to Azure CLI.
-
Install Argo CD CLI.
-
From the terminal, log in to the Argo CD server:
Argo CD login --sso [Argo CD-server-fqdn] -
Add the application using the following Argo CD CLI command:
Argo CD app create [app-name] \
--repo [link-to-added-repository] \
--path [path-to-an-application] \
--dest-namespace [destination-namespace] \
--dest-server "https://$(az aks show --name [cluster-name] --resource-group [cluster-name] --query fqdn --output tsv):443" \
--project [your-project-name] \
--values [values-file-name]
Example
To onboard the Helm application from the specified repository targeting workshop cluster, the user should use the following command:
Argo CD app create aurora-flask-app \
--repo git@github.com:equinor/aurora-k8s-usecases.git \
--path helm \
--dest-namespace aurora-flask-app \
--dest-server "https://$(az aks show --name dev-aurora-workshop-00 --resource-group dev-aurora-workshop-00 --query fqdn --output tsv):443" \
--project workshop \
--revision golden-template-adoption \
--values values.yaml
Please note that proper RBAC must be configured to execute the application creation command. If you encounter any issues, contact #ai_platfrom_support.
Using Workload Identity to get an Azure Entra ID token
In some cases, developers may need to obtain an Azure Workload Identity token.
The sample application Helm chart is adapted to support the setup of Workload Identity.
From a terminal, follow these steps:
- Define variables.
APPLICATION="[application-name]"
CLUSTER_NAME="[aurora-cluster-name]"
IDENTITY_NAME="[workload-identity-name]"
IDENTITY_RESOURCE_GROUP="[workload-identity-resource-group]"
NAMESPACE="[workload-namespace]"
SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME="[service-account-name]"
IDENTITY_NAME="[user-assigned-identity-name]"
- Create a user-assigned managed identity.
az identity create --name "${IDENTITY_NAME}" --resource-group "${IDENTITY_RESOURCE_GROUP}"
- Create a federated identity credential.
az identity federated-credential create \
--identity-name "${IDENTITY_NAME}" \
--issuer $(az aks show --name "$CLUSTER_NAME" --resource-group "$IDENTITY_RESOURCE_GROUP" --query oidcIssuerProfile.issuerUrl --output tsv) \
--subject "system:serviceaccount:${NAMESPACE}:${SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}" \
--audiences "api://AzureADTokenExchange" \
--resource-group "${CLUSTER_NAME}" \
--name "${APPLICATION}"
-
Patch the Helm chart values file with a values required for workload identity (check comments on the file).
-
Run the following command from the pod shell to test the identity assignment (Azure CLI should be installed on the pod)
az login \
--service-principal \
-u $(az identity show --name "$IDENTITY_NAME" --resource-group "$IDENTITY_RESOURCE_GROUP" --query clientId --output tsv) \
--federated-token "$(cat $AZURE_FEDERATED_TOKEN_FILE)" \
-t $(az account show --query tenantId --output tsv)
Accessing the application
Depending on what you specified in the virtualServicePath Helm chart value, your application will be accessible at the following URL: https://[cluster-fqdn]/[virtualServicePath-variable-value]/
We use Istio on AI Platform, so the ingress controller and ingress rules are managed through its resources.
All AI Platform cluster domains are secured with authorization, and only Equinor members with AI-Platform-Developer or AI-Platform-User access will be allowed to access the resources.
If you require a different configuration, please contact #ai_platfrom_support.